Infrastructure Documentation
This document outlines the infrastructure architecture and deployment approach for the Provfair gaming platform. The system runs on AWS using containerized services with automated scaling and management.
The Provfair gaming platform runs on AWS using containerized microservices with automated scaling, multi-zone redundancy, and comprehensive monitoring. The architecture includes MongoDB Atlas for data persistence, Redis for caching, and CloudFront for global content delivery. All infrastructure is managed as code with automated deployments, backup strategies, and security controls.
Enterprise-Level Architecture Benefits:
- High Availability: Multi-zone deployment with automatic failover and 99.99% uptime target
- Scalability: Auto-scaling containers handle traffic spikes from thousands to millions of users
- Security: IAM roles, encrypted data, secrets management, and compliance monitoring
- Observability: Distributed tracing, structured logging, and real-time performance metrics
- Disaster Recovery: Automated backups, cross-region replication, and infrastructure as code
- Cost Efficiency: Spot instances for non-critical workloads and automated resource optimization
Platform Architecture
Simplified Flow Chart
Detailed Infrastructure Diagram
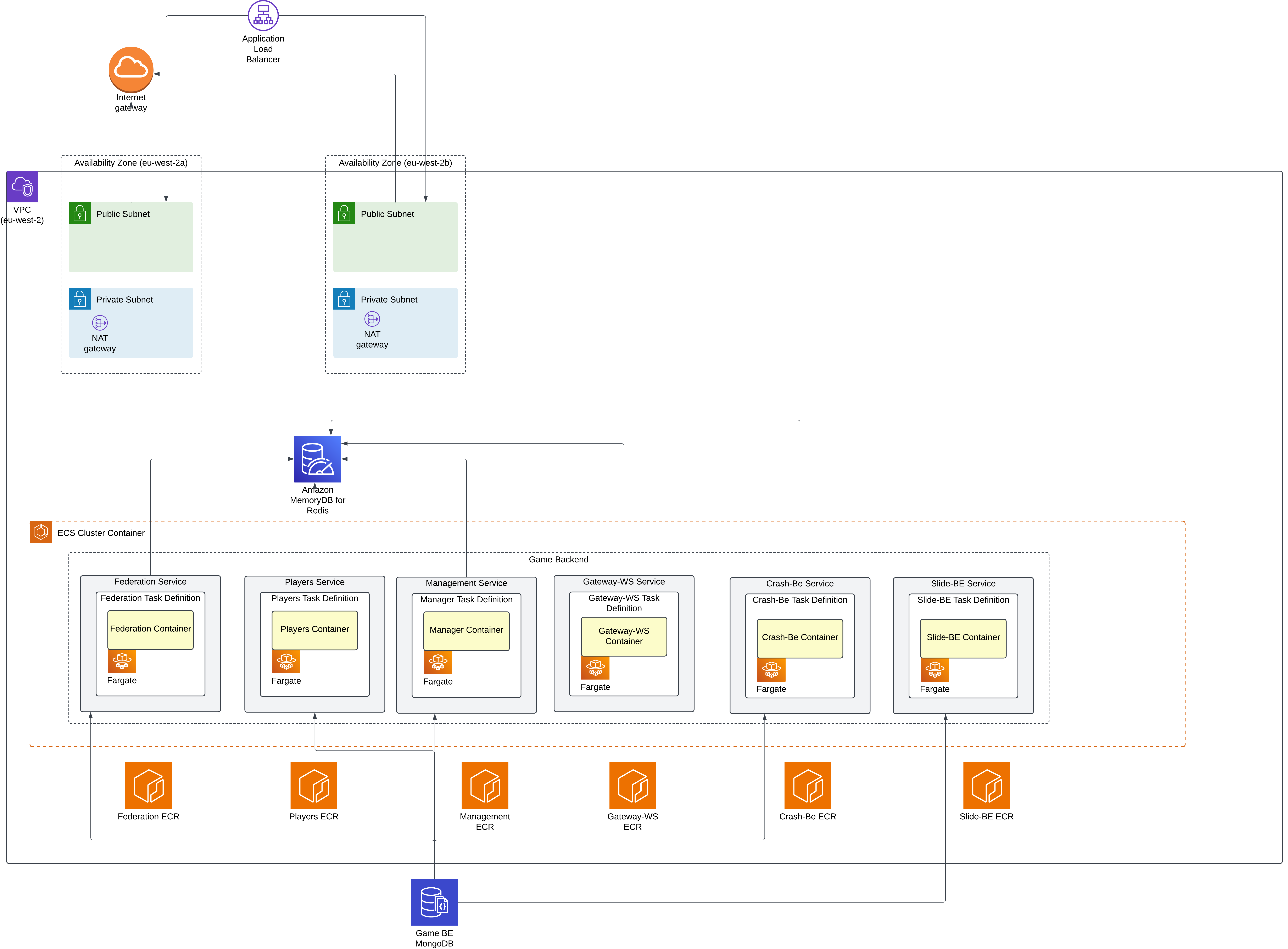
Network Design
The platform uses a Virtual Private Cloud with separate public and private subnets distributed across two availability zones. An Application Load Balancer handles incoming traffic and routes requests to appropriate services. Security groups provide layered network access controls, while AWS Cloud Map enables service discovery between internal components.
Container Management
The system uses Alpine Linux base images to reduce the attack surface. Docker images are built using multi-stage processes to optimize size and exclude build dependencies from production containers. Each service includes health check endpoints for monitoring, and the platform can automatically scale services based on CPU and memory usage patterns.
High Availability
Services are distributed across multiple availability zones to ensure continued operation during infrastructure failures. Automatic scaling groups manage capacity based on demand, while rolling deployments allow updates without service interruption. Circuit breaker patterns help prevent cascading failures between services.
Infrastructure as Code
Management Approach
The infrastructure uses Pulumi for declarative resource management. This approach tracks all infrastructure changes in version control, allowing teams to review modifications before deployment and maintain rollback capabilities when needed.
Environment Management
The system supports multiple environments through configuration files that specify resource names, sizes, and networking parameters for each deployment target. Resources are automatically tagged for cost tracking and organizational purposes.
Resource Deployment
Services are deployed through automated pipelines that create containerized applications with specified CPU and memory allocations. Environment variables and secrets are loaded from secure storage during deployment.
Service Configuration
Container Services
Each microservice runs as an independent containerized service with dedicated resource allocations ranging from 256 to 1024 CPU units and 512MB to 2GB of memory depending on workload requirements. Services typically run 2-10 container instances for availability and can be adjusted based on traffic patterns.
Scaling Behavior
Services automatically scale between minimum and maximum capacity limits based on CPU utilization metrics. When average CPU usage exceeds 70% for sustained periods, additional containers are started. The system includes cooldown periods to prevent rapid scaling oscillations.
Network Configuration
The platform uses a Virtual Private Cloud with a 10.0.0.0/16 address range distributed across two availability zones. Public subnets host load balancers and NAT gateways, while private subnets contain application services. Each availability zone has its own NAT gateway for outbound internet access.
Security Controls
Security groups control network access at the service level. Application services accept HTTP traffic on port 80 and HTTPS traffic on port 443 from the internet, while internal communication between services uses specific port ranges. All outbound traffic is permitted to support external API calls and software updates.
Load Balancing
An Application Load Balancer distributes incoming requests across healthy service instances. The load balancer terminates SSL connections using managed certificates and routes traffic based on request paths. Each service has a dedicated target group that monitors service health through HTTP endpoints and removes unhealthy instances from rotation.
Database and Storage
Primary Database
The platform uses MongoDB Atlas as the primary database service. The production cluster runs MongoDB 6.0 on M30 instance sizes configured as a replica set with three nodes in the US East region. This setup provides automatic failover capabilities and read scaling options.
Caching Layer
Redis ElastiCache provides distributed caching and session management. The cluster consists of three cache nodes running Redis 7 on r6g.large instances with automatic failover enabled. The cluster is distributed across multiple availability zones for fault tolerance.
Monitoring and Logging
Log Management
Application logs are collected in CloudWatch Log Groups with a 30-day retention period. Logs are structured in JSON format to enable efficient searching and analysis. Each service maintains separate log streams for better organization.
Performance Monitoring
CloudWatch Alarms monitor key metrics including CPU utilization, memory usage, and request latency. Alarms trigger when CPU usage exceeds 80% for two consecutive 5-minute periods, enabling proactive response to performance issues.
Distributed Tracing
AWS X-Ray provides distributed tracing capabilities to track requests across service boundaries. OpenTelemetry collectors gather performance metrics and traces from applications, providing detailed insights into system behavior and bottlenecks.
Security Implementation
Access Control
IAM roles follow the principle of least privilege, granting services only the permissions needed for their specific functions. Task execution roles allow containers to pull images and write logs, while application roles provide access to required AWS services like databases and message queues.
Secrets Management
AWS Secrets Manager stores sensitive configuration data including database credentials, API keys, and encryption keys. Secrets are automatically rotated when possible and are injected into containers at runtime rather than being embedded in images or configuration files.
Backup and Recovery
Data Protection
Automated backups run daily at 2 AM UTC, storing data in AWS Backup vaults with 30-day retention. Database snapshots are encrypted using customer-managed KMS keys and stored across multiple availability zones. Point-in-time recovery is available for databases within the backup retention window.
Geographic Distribution
A secondary infrastructure deployment exists in the US West region for disaster recovery purposes. This standby environment can be activated manually if the primary region becomes unavailable. Cross-region replication keeps backup data synchronized between regions.
Cost Management
Resource Organization
All resources are tagged with project, environment, owner, and cost center information to enable detailed cost tracking and budget allocation. Regular cost analysis helps identify opportunities for optimization and ensures resources are appropriately sized for their workloads.
Cost Optimization
Non-critical workloads use spot instances when available, providing significant cost savings. Services automatically scale down during low-usage periods, and unused resources are identified and decommissioned through regular audits.
Performance Optimization
Content Delivery
CloudFront provides global content distribution with edge locations worldwide. Static assets are cached at edge locations to reduce latency for users regardless of their geographic location. The CDN configuration redirects all traffic to HTTPS and uses optimized caching policies for different content types.
Compliance and Governance
Configuration Management
AWS Config tracks configuration changes across all resources and can detect deviations from established security baselines. Configuration recording captures all supported resource types including global resources to maintain a complete audit trail.
Compliance Monitoring
Automated compliance rules check for security best practices such as encrypted storage volumes, proper security group configurations, and appropriate access controls. Non-compliant resources trigger alerts for immediate remediation.
Summary
The infrastructure supports a containerized gaming platform with automated scaling, monitoring, and security controls. The architecture prioritizes availability through multi-zone deployment and includes comprehensive backup and recovery procedures. Resource management through infrastructure as code enables consistent deployments and facilitates maintenance across environments.